Acne vulgaris is a skin condition that occurs when pores or hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
The outbreak of lesions, such as whiteheads, blackheads, and pimples, requires different treatments based on their root cause and severity. Persistent inflammatory acne may also lead to scarring and cause emotional distress.
While acne typically affects teens and young adults, any age group can develop the condition.
This article gives a rundown of acne symptoms, types, causes, and treatment options.

What is Acne?
Skin breaks out in acne when pores or hair follicles become clogged with excess oil (sebum), dead skin cells (keratinocytes), or dirt.
Sebaceous (oil) glands produce a natural oily substance that protects and hydrates the skin. However, too much sebum can stick to keratinocytes and dirt inside the pores, resulting in the buildup of dead skin, follicle blockage, and irritation.
Inflammatory acne develops when skin bacteria (Cutibacterium acnes) enter a clogged follicle, break the pore’s walls, and cause infection that spreads to the surrounding areas.
Acne Symptoms
Acne signs vary depending on the severity, acne type, and the underlying cause.
The following are the most common acne symptoms:
- Small, dark-colored spots
- Small, white-colored spots
- Red, tender spots
- Zits or blemishes
- Rough, uneven skin texture
- Skin discoloration
- Flaky or peeling skin
- Increased skin sensitivity
- Excessively oily skin
- Swollen bumps
- Red, inflamed pimples
- Large, solid lumps
- Painful, pus-filled lumps or cysts
- Flesh-colored lumps underneath the skin
Note: Read about 7 ways to get rid of oily skin and prevent further breakouts.
Areas Commonly Affected by Acne
Acne breakouts can affect any part of the body. The areas most prone to acne include:
- Face
- Neck
- Shoulders
- Back
- Chest
Types of Acne
There are two basic types of acne based on their severity and formation - inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
Non-inflammatory, mild acne, also known as comedones, includes whiteheads (closed plugged pores with a flesh-colored top) and blackheads (open plugged pores with a black top).
Inflammatory acne is a more severe skin inflammation condition that can cause swelling, irritation, and infection. This type is more likely to leave scarring or cause permanent skin damage.
The most common inflammatory acne types are the following:
- Papules - Red, swollen bumps with no pus.
- Pustules - Swollen or firm bump with white or yellow pus.
- Nodules - Painful, red, or flesh-colored lumps underneath the skin.
- Cysts - Red or white painful lumps filled with pus.
Note: Take a closer look at types of acne, how they differ, and what treatment method to adopt.
What Causes Acne?
Various factors provoke acne flareups or worsen the condition. Triggers can be internal or external, or a combination of both. It is essential to discover what causes acne before attempting to eliminate or repair skin damage.

Physical Triggers
The most prominent external or physical causes for acne breakouts are the following:
- Hair follicle blockage – Clogged pores may occur due to sebum overproduction, excessive or hormonal sweating, and the buildup of dead skin cells.
- Bacterial overgrowth – When the skin’s natural surface bacteria (e.g., Cutibacterium acnes) multiply or spread to surrounding areas, the skin becomes red, tender, and inflamed.
- Inappropriate skincare products – Harsh, irritant cosmetics can clog pores and aggravate your skin condition. An expert skincare guide can help you understand what products to use for your skin type and how to identify comedogenic (pore-clogging) ingredients.
- Environmental factors - Overexposure to pollutants and high humidity can lead to the accumulation of dirt and toxins, which clogs the pores and forms comedones.
- Friction, pressure, or rubbing – Applying too much pressure on the epidermis can damage the protective outer skin layer, increasing the risk of a bacterial acne-causing infection.
Note: Learn more about inflammation and how to reduce it effectively.
Psychological Triggers
Chronic stress impacts overall health and skin quality. Prolonged exposure to daily stressors may lead to or worsen various skin disorders, including eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
Acne breakouts occur when elevated cortisol levels increase sebum production. Cortisol, the so-called “stress hormone”, prepares the body for a perceived threat.
Excess sebum clogs the pores, contributes to acne formation, and prolongs healing. This environment may also worsen the condition due to bacteria proliferation.
Note: Learn more about how stress influences skin quality and ways to treat stressed skin.
Foods
There is no conclusive scientific evidence about specific food groups or diet plans that directly cause or prevent acne vulgaris.
However, studies show that high-glycemic foods may worsen the condition and contribute to associated health conditions, such as obesity and insulin resistance. Foods with a high glycemic index include processed foods, white bread, pastry, corn, grapes, watermelon, mango, banana, etc.
On the other hand, low-glycemic foods decrease glycemic load and eliminate blood sugar spikes responsible for sebum production and more frequent acne breakouts. Skin-friendly food choices include non-starchy vegetables, greens, apples, raw carrots, berries, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., salmon, chia seeds).
Note: Learn how insulin resistance affects weight loss.
Medication
Certain types of medication can induce acne eruptions or aggravate the condition. These include but are not limited to:
- Corticosteroids
- Androgenic steroids
- Birth control pills
- Thyroid hormones
- Antibiotics tetracycline and streptomycin
- DHEA supplements
- Drugs containing bromides, iodides, or lithium
- Anticonvulsants
- Some anticancer drugs
Some medicine-related skin flareups are difficult to differentiate from acne. For example, acneiform drug reactions only resemble acne and require medical assistance and evaluation.
Hormones
Hormone-related acne develops due to an imbalance in the production of estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone.
Hormonal fluctuations may activate excess sebum production that clogs the pores, producing bumps, lumps, and skin lesions. Depending on the severity and type, hormonal acne can be both inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
The most common causes for a hormone-triggered acne breakout are the following:
- Puberty
- Menstruation
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Perimenopause
- Menopause
- Thyroid issues
- Increased levels of androgen
Some patients benefit from over-the-counter topical solutions, while others turn to hormone-balancing supplements and hormone replacement therapies to clear acne and manage symptoms.
Acne Myths
There is a lot of misinformation regarding acne formation, causes, and treatments. It is vital to debunk the most persistent acne-related myths to understand this skin condition.
The most common acne-related fallacies are the following:
- Acne only affects teenagers and young adults.
- Poor hygiene or dirt causes acne.
- Acne is contagious.
- Sun exposure clears acne.
- Popping or squeezing pimples speeds up the recovery.
- Greasy food and chocolate cause acne.
- Washing your face more frequently can reduce acne.
- Toothpaste can clean small acne breakouts.
- Acne will go away on its own and does not require treatment.
These common misconceptions can worsen the condition, inflame the skin, and cause stronger flareups. Consulting an experienced dermatologist can speed up the recovery and help remove doubts about proper treatment solutions.
Who Can Get Acne?
While it is more prevalent in teenagers and young adults, acne can affect people of all ages, genders, and ethnic backgrounds.
Studies show that 85% of people between the ages of 12 and 24 struggle with acne, while 25% of women and 12% of men report acne in their forties.
Hormonal disruptions, lifestyle choices, and genetics contribute to this type of skin condition that can develop or persist at any life stage.
How Is Acne Diagnosed?
Acne vulgaris requires medical assistance and an evaluation of the severity of the lesions. Your primary care physician will refer you to a dermatologist who will identify the acne type and the underlying cause.
The routine examination includes checking the patient’s medical record, current medication, hormone therapies, and skincare products. The doctor will discuss your symptoms and perform a physical examination to determine acne type and severity.
They may also run additional blood tests that point to higher levels of acne-triggering hormones, such as testosterone.
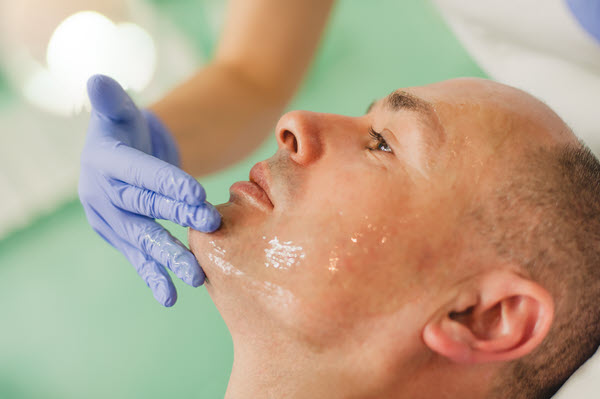
How to Treat Acne
Treatment requires a previous diagnosis of the acne type, cause, and severity of symptoms. The approach depends on the patient’s skin type, current skin condition, and tolerance for specific medications or therapies.
- Acne facials – Acne facial treatments treat mild to moderate acne types (whiteheads, blackheads, papules, and pustules). Vibrant Skin Bar skin experts achieve lasting results with Acne Eraser Facial, which consists of four steps: cleansing, extraction, exfoliation, and serum treatment.
- Medical-grade skincare products – Medical-grade skin products with non-comedogenic, anti-inflammatory ingredients, such as Let’s Get Clear acne mask or Osmosis MD Clarify Blemish Retinal Serum, help calm, protect, and hydrate acne-prone skin.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) topical solutions - For mild, non-inflammatory acne, you use OTC creams, lotions, cleansers, and gels that contain benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, sulfur, and resorcinol. These ingredients help remove dead skin cells and excess sebum.
- Prescription topical solutions – Topical antibiotics, retinoids, azelaic acid, and dapsone prevent or minimize moderate to severe acne breakouts. They remove dead skin cells, fight off bacteria, or reduce inflammatory acne (e.g., papules or pustules).
- Prescription oral medications – Doctors prescribe oral antibiotics and retinoids alone or in combination with topical treatments for severe acne, such as cysts or nodular acne. They prevent further infection and scarring.
- Steroid injections – Corticosteroid injections reduce inflammation in severe forms of acne, such as cysts and nodules.
- Hormone therapies – Hormone replacement therapies rebalance disrupted hormones that cause skin breakouts during hormonal shifts, such as perimenopause or menopause.
- Light therapies – Photofacial treatments use pulsating red or blue light technology to reduce skin inflammation, eliminate acne-causing bacteria, and soothe irritated skin.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT) – This innovative acne treatment utilizes a photosensitizer in combination with intense pulsed light and oxygen to reduce acne and clear the complexion.
- Laser therapy – Laser beams and pulsed light used in non-invasive BBL laser treatments and Forever Clear®️ acne laser series can be used to kill bacteria and stimulate the growth of new skin.
Note: Get more recommendations of the best skincare products for oily acne-prone skin.
Consequences of Acne
Problems with acne peak during adolescence and usually subside over time. However, acne can persist into adulthood and develop into a long-term health condition that is not purely cosmetic or aesthetic.
Without timely or appropriate treatment, acne can develop into severe lesions, nodules, or cysts. These acne types leave permanent skin damage, such as scarring or hyperpigmentation.
Acne scars can lower self-esteem and cause emotional distress, too. Luckily, there are effective acne scar treatments. These include:
Conclusion
Acne is a great challenge to anyone struggling to maintain healthy, glowing skin. Without an adequate skincare routine and professional help, this issue can quickly spiral out of control. Therefore, seeking expert advice before attempting to treat the condition is essential.
Contact the Vibrant Skin Bar skin experts for more information about available acne treatments in the Phoenix area.




