Inflammation is a natural-occurring healing process triggered by the immune system. However, when disrupted, it can cause skin problems that affect both men and women.
Persistent, long-term skin inflammation can manifest in many forms, including rashes, redness, itching, swelling, or pain. Causes range from harsh chemicals, allergens, and infections to autoimmune disorders like psoriasis.
This article discusses the types, symptoms, and causes of skin inflammation and presents available treatment options.

What Is Skin Inflammation?
Skin inflammation, also known as dermatitis, is caused by an immune system that becomes overactive in its attempt to neutralize a foreign agent, such as allergens, irritants, bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Certain autoimmune conditions, such as psoriasis, lupus, or celiac disease, might also trigger an inflammatory response.
The body’s defense mechanism sends out inflammatory mediators in response to a perceived threat, causing the skin to break out in pimples, blisters, or red patches. Symptoms can be mild and temporary or chronic and recurring. The latter require medical assistance and a robust treatment strategy, including antibiotics, topical medication, immune-boosting therapy, and light therapy.
Types of Skin Inflammation
There are two distinct types of skin inflammation that differ in terms of cause, duration, and effects:
1. Acute Skin Inflammation
This type involves a short-term inflammatory process triggered by external irritants. Typical examples include:
- Sunburn
- Damage due to heat exposure
- Acne
- Blisters
- Hives (urticaria)
- Allergic reaction (contact dermatitis)
- Insect bite reaction
- Bacterial, viral, or fungal infection
Symptoms may vary in intensity, lasting for a few hours up to six weeks. They include redness, rashes, dry skin, peeling, redness, itching, or swelling. Symptoms are typically localized, leaving no permanent tissue damage.
Treatments involve steroid creams, antihistamines, anti-itch ointments, wet and cold compresses, or prescription medication.
2. Chronic Skin Inflammation
This is an extended inflammatory reaction worsened by internal, long-term factors, such as autoimmune disorders. Common examples include:
- Eczema (e.g., atopic, dyshidrotic, or seborrheic dermatitis)
- Psoriasis (e.g., plaque, pustular, or inverse psoriasis)
- Rosacea (e.g., phymatous or papulopustular rosacea)
- Dermatomyositis
- Impetigo (non-bullous and bullous type)
- Vitiligo (generalized and non-segmental type)
These chronic skin conditions can persist for years, leading to potential tissue damage. They produce recurring symptoms such as skin discoloration, red patches, flakiness, scaling, itchiness, and prolonged flare-ups.
Treatments include topical steroid creams, corticosteroids, moisturizers, antihistamines, light therapy, and more.
Note: Read about the 13 most effective holistic eczema treatments.
Skin Inflammation Symptoms
Depending on the cause and severity of the irritation, inflamed skin may show some of the following symptoms:
- Rashes
- Dryness
- Redness
- Itching
- Scaling
- Lesions
- Sores
- Warmth or heat
- Pain
- Stinging
- Burning
- Swelling
- Blisters
- Pus
- Pimples
- Hives
- Plaques
- Skin thickening
- Raw or cracked skin
- Bleeding
- Discoloration
- Photosensitivity
Symptoms are non-contagious unless caused by a viral or bacterial infection. Staying away from allergens and irritants might alleviate them, while consistent treatment targets the underlying cause.
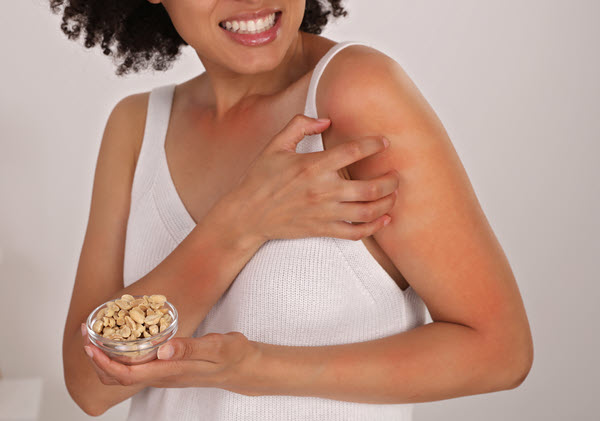

Skin Inflammation Causes
You can learn how to reduce inflammation by discovering its root cause. Potential skin inflammation triggers include:
1. Allergic Reaction
Contact dermatitis, the most common type of acute skin inflammation, is an allergic reaction to external stimuli resulting in a skin rash or hives. It occurs when the immune system overreacts to irritants, such as harsh chemicals, cosmetic products, perfumes, poison ivy, pollen, dust mites, and certain foods.
2. Bacterial, Viral, or Fungal Infection
When bacteria, viruses, and fungi proliferate, they may trigger the body’s defense mechanism that is biologically designed to fight off the invading pathogens.
Some inflammatory reactions are contagious, such as impetigo, a bacterial skin infection causing sores and blisters, or ringworm, a fungal skin infection that leaves characteristic ring-shaped lesions.
Others are non-contagious, such as cellulitis, a bacterial skin infection resulting in painful, discolored skin, or seborrheic dermatitis that causes dandruff-like flaky patches.
3. Insect Bites and Stings
Insects such as mosquitos, fleas, ticks, or bees release saliva or venom when they bite or sting, causing the skin to become red, swollen, itchy, or painful. The immune system detects the injury and sends inflammatory cells to repair the tissue damage.
If the reaction persists for several days or develops into anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction), it requires immediate medical treatment.
4. Photosensitivity
Direct sun exposure can rev up the immune system, initiating a strong inflammatory response that results in red spots. This is a typical reaction for people who are extremely sensitive to light, a common symptom of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). It is also known as sun allergy or solar urticaria.
5. Environmental Factors
Skin can become inflamed due to excessive heat or sun exposure, leading to burns, blisters, and swelling. Hot and humid weather can cause a heat rash, also known as prickly heat, manifesting as itchy, blister-like bumps that are sometimes filled with pus. Hot external stimuli such as food, drinks, a gas stove, or boiling water can cause heat urticaria, resulting in weals or cutaneous lesions.
Conversely, freezing weather or cold intolerance may trigger a medical condition known as cold urticaria, with welts, swelling, or itchy rash.
Note: Read about the 10 best ways to treat sunburn, reduce skin inflammation, and prevent premature aging of the skin.
6. Immune Dysfunction
Certain immunological disorders can prolong the inflammatory reaction, worsening the existing skin condition. These include:
- Psoriasis – Increased skin cell production resulting in dry patches covered in scales called plaques.
- Cutaneous lupus – An overactive immune system targets skin cells, causing red, scaly rashes and burning itchy sores.
- Dermatomyositis – An inflammatory disease characterized by a skin rash that may also be accompanied by progressive muscle weakness.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis – An autoimmune reaction to gluten that elevates antibodies (IgA), producing itchy bumps and blisters.
- Scleroderma – A connective tissue disorder that overstimulates collagen production to produce tight, hard, or discolored skin.
7. Medication
Both prescription and over-the-counter medication can trigger cutaneous (skin-related) adverse reactions. Antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and NSAIDs are the most common rash-causing medications.
Drug rashes may appear as changes in skin color or texture, breakouts, peeling, blistering, and bumps. The reaction can be immediate, but it may also develop after several days or weeks.
8. Emotional Stress
Chronic stress affects skin quality in many ways, worsening existing skin conditions (acne) or triggering new ones (rosacea, psoriasis, eczema). A weakened immune system makes the skin barrier more sensitive and reactive, leading to frequent flare-ups, fever blisters, and hives. Extreme or sudden stress may also activate hereditary diseases, such as vitiligo.
9. Physical Trauma
Excessive scratching, rubbing, and physical injuries, such as burns, cuts, and abrasions, activate a proinflammatory healing process. The affected area becomes red, swollen, and hot due to increased blood flow initiated by the inflammatory wound-repairing system.
10. Chronic Skin Conditions
Long-term skin conditions contribute to frequent skin irritations and flare-ups, provoking extended inflammation.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, can cause inflamed, itchy, rough, and cracked patches or even blisters, while rosacea results in swollen bumps, flushing, visible veins, and a burning sensation.
11. Genetic Predisposition
Skin sensitivity can be a hereditary trait. Some people are genetically more susceptible to developing chronic skin conditions or displaying strong cutaneous reactions. Hereditary skin disorders include eczema (atopic dermatitis), psoriasis, or dermatographia, a condition characterized by raised, inflamed lines, swelling, itching, or welts caused by light scratching or friction.
12. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalance can activate excessive oil production (sebum), leading to clogged pores and inflammatory acne. Acne can be painful and persistent, and are likely to leave scars.
Note: Learn about the best acne scar treatments.

How Is Skin Inflammation Diagnosed?
Timely, accurate diagnosis of skin inflammation can reverse and prevent some damage. The most common diagnostic steps consist of:
- Checking the patient’s medical history – The medical record may indicate risk factors based on genetic predisposition and past medical conditions.
- Performing a physical exam – The doctor identifies the skin inflammation type and severity by closely inspecting the affected area.
- Routine blood testing – Different blood tests can establish whether a pre-existing autoimmune condition is the underlying cause of the skin issue.
- Allergy testing – Blood sampling detects antibodies to specific allergens, while a skin test checks allergic reactions to small doses of the injected allergen.
- Skin biopsy – This optional step involves taking a small skin sample to examine it under a microscope.
Skin Inflammation Treatment
Dermatologists recommend practicing a skin care routine tailored for sensitive, breakout-prone skin while avoiding allergens, triggers, and irritants. If these preventive measures don’t yield satisfactory results, you can try out some of the following treatments based on the underlying cause, symptoms, and skin type.
Note: Check out our selection of the best products for sensitive skin.
Oral Medication
Prescription and off-the-counter medication can alleviate symptoms by targeting the cause of a particular skin reaction. This type of medication includes:
Antihistamines
During an allergic reaction, the immune system releases a symptom-causing chemical called histamine. Antihistamine drugs block histamine to reduce the symptoms, such as itching, redness, hives, or swelling.
NSAIDs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are pain-relieving capsules and tablets used to reduce inflammatory reactions, such as tenderness, pain, or swelling. Common NSAIDs used for dermatitis are ibuprofen, diclofenac, and aspirin.
Antibiotics
Doctors prescribe antibiotic medication to treat bacterial skin infections, such as cellulitis or impetigo. Typical oral antibiotics include dicloxacillin, cephalosporins, clindamycin, and vancomycin. Severe cases of acne can also be treated with antibiotics such as tetracycline.
Antifungal Medication
Athlete’s foot, jock itch, ringworm, or yeast infections are types of fungal skin conditions that require antifungal medication. These medicines work by eliminating the fungus and preventing it from growing.
Systemic Medication
Oral immunosuppressants can effectively reduce skin inflammation if the underlying cause is an autoimmune disease, such as scleroderma, psoriasis, eczema, or dermatomyositis. The most common immunosuppressive drug is methotrexate.
Topical Treatments
Topical anti-inflammatory medication is directly applied to irritated skin. It comes in the form of creams, gels, and lotions.
Moisturizes, Creams, and Serums
Antioxidant skincare products contain active ingredients, such as resveratrol, that protect the skin from free radicals by strengthening the skin barrier, decreasing skin sensitivity, and fighting inflammation.
- Osmosis MD Rescue Epidermal Repair Serum calms inflammation by neutralizing toxins to enhance epidermal care and DNA repair.
- iS CLINICAL Copper Firming Mist provides powerful antioxidant skin protection and supports the compromised skin barrier.
- Osmosis MD Replenish Antioxidant Infusion Serum minimizes inflammation caused by environmental factors, such as sun exposure, pollution, ozone, or smoke.
- Osmosis MD Clarify Blemish Retinal Serum promotes wound repair, decreases inflammation, and promotes blemish clearing with retinaldehyde.
Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroid creams, lotions, gels, mousses, and ointments reduce skin irritation through direct application. They vary in potency, providing mild, moderate, or strong treatment options for eczema, contact dermatitis, or psoriasis.
Immunomodulators
Topical immunomodulators target the dysregulated immunological pathways to treat dermatological diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, alopecia areata, vitiligo, or psoriasis. They either suppress or upregulate the immune response to combat the signs of inflammation.
Light Therapy
Phototherapy employs ultraviolet light to treat skin conditions, including dermatitis, vitiligo, eczema, and psoriasis. Red light therapy targets wrinkles, redness, and inflammation with low-level wavelengths. Blue light therapy is efficient in treating acne-prone skin, reducing redness, and promoting cellular turnover.
Both types of phototherapy contribute to vitamin D synthesis, which activates the skin’s natural anti-inflammatory properties and kickstarts the healing process. Light therapy also prevents excessive skin cell growth and provides an effective antibacterial treatment.
Note: One session of red light therapy at Vibrant Skin Bar costs $45. Contact us to find out if you're a good candidate and book an appointment.
Home Remedies
You can relieve mild to moderate skin irritation with homemade, plant-based solutions. Some symptoms are short-lived and easy to remove with the following:
- Cold compresses – You can reduce redness, swelling, and itching with cold and wet compresses, ice packs, and a cold bath.
- Anti-inflammatory diet – Adopt a diet packed with hypoallergenic foods that reduce inflammation, such as cucumbers, carrots, broccoli, apples, pears, and lamb.
- Mild skincare – Use skincare products for sensitive skin with hypoallergenic, natural ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, coconut oil, or shea butter.
- Aloe vera – This natural moisturizer rehydrates dry skin, protecting it with its wound-healing, antiseptic, and anti-viral properties.
- Tea tree oil – Its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory qualities reduce itching and irritation. It is especially beneficial for seborrheic dermatitis and acne.
- Chamomile oil – Matricaria (chamomile) has many healing, antioxidant aspects and a soothing effect perfect for sensitive skin types.
- Calendula (marigold) – Marigold tinctures, ointments, and infusions treat wounds and reduce acne, rashes, and blemishes. Calendula acts as a natural astringent and has a potent antiseptic effect.
If the inflammation persists or gets worse, consult a dermatologist for further treatment.
Note: Read about the best natural skincare routine with product recommendations for each step.
Skin Treatments
Skin treatments can reduce skin inflammation by removing built-up dirt, unclogging pores, exfoliating, and cleansing with medical-grade, allergen-free products. Here are some of the treatments we offer at Vibrant Skin Bar:
- Holistic facials are particularly effective due to their gentle, non-invasive approach. They can help with rosacea, psoriasis, eczema, and acne.
- Skin Rehab includes face mapping and a personalized skincare program aimed at healing the inflammatory reaction of acne-prone skin.
- Remedy Facial, tailored for sensitive, inflamed skin, contains Vibrant Skin CBD Recovery Mask with strong pain-relieving, antioxidant properties that support the skin’s immune system.
Note: Read our article about all the elements of holistic skin care.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Consult a dermatologist if the rash starts spreading to other areas, or if the swelling, itching, and redness intensify.
Seek immediate medical treatment in case of:
- High fever
- Blisters
- Pus
- Oozing
- Bleeding
Conclusion
Accurate diagnosis of skin inflammation can help manage the symptoms and reduce flare-ups. Effective treatment may repair the skin damage and provide protection against potential inflammatory triggers.
Contact the Vibrant Skin Bar team of skin experts for more advice.


