Lasers are narrow, focused beams of light that have been used for decades for cutting and welding, scanning barcodes, carrying internet signals, and many other things. Their clinical application began in the 1980s, marking a breakthrough in the treatment of various medical conditions.
This article explains how laser therapy is used in medicine and the cosmetics industry and how patients can benefit from the procedure.
What Is Laser Therapy?
Laser therapy is a procedure in which a beam of light penetrates the skin to treat damaged tissue. It is a very precise and intense beam that converts to heat when absorbed by water, melanin, or hemoglobin in the treatment area. This heat energy makes structural changes to tissues and cells.
Laser light consists of waves with similar wavelengths. These specific wavelengths in medical lasers range from approximately 400 to 10,600 nm, depending on the treatment and how deep the light needs to penetrate.
Types of Laser Therapy
Laser therapy can be categorized in two main ways:
1. Laser Therapy by Application
Laser therapy can be grouped based on its intended medical or cosmetic use. This classification highlights how lasers are applied in treatments ranging from cancer care to cosmetic skin rejuvenation.
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
PDT combines a laser with a photosensitizing drug that becomes active under light exposure. It is used to destroy cancerous cells, treat certain skin conditions, and address other medical concerns.
Laser Surgery
This minimally invasive method uses concentrated light to make precise cuts, shrink or remove tumors, seal blood vessels, and reshape tissues (e.g., corneal correction).
Laser Resurfacing
A cosmetic procedure that removes damaged skin layers and stimulates tissue remodeling, reducing wrinkles, scars, age spots, and other visible signs of aging.
2. Laser Therapy by Device Type
Laser treatments are also categorized by the type of laser device used. Each laser has unique properties, such as wavelength, penetration depth, and tissue interaction, that determine its suitability for specific procedures.
Medical Lasers
- CO₂ Lasers – Remove thin layers of skin or tissue, often used for surface tumors.
- Argon Lasers – Commonly applied in PDT; penetrate thin layers of skin and tissue.
- Nd:YAG Lasers – Reach deeper tissue, treat vascular abnormalities, control bleeding, and are safer for darker skin types.
- LITT (Laser Interstitial Thermotherapy) – Targets spaces between organs to heat and shrink tumors.
Cosmetic Lasers
- Ablative Lasers – Vaporize the outer skin layer and heat dermis for collagen stimulation (e.g., CO₂, Er:YAG).
- Non-Ablative Lasers – Stimulate collagen without removing outer layers, less invasive (e.g., BBL, IPL, pulsed dye, Nd:YAG, Moxi).
- Fractional Lasers – Split beams into micro-zones, treating partial areas of skin for faster recovery (e.g., Fraxel, fractional CO₂, Er:YAG, Moxi).
- Hybrid Lasers – Combine ablative and non-ablative technologies for comprehensive rejuvenation (e.g., Halo, Alma Hybrid).
Note: Learn about the differences between BBL and MOXI Laser.
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for Laser Therapy?
The decision whether a patient is a candidate for laser therapy is made on a case-by-case basis. The medical provider assesses the patient’s medical history and health status to determine if laser treatment is an adequate solution.
For example, potential laser eye surgery candidates need to have good eye and overall health and be at least 21 years old. Many patients with pre-cancer and early cancer are candidates for laser cancer therapy. Other medical concerns treated with laser include musculoskeletal disorders, dental issues, fibromyalgia, and other chronic pain conditions.
Patients interested in laser resurfacing for aesthetic reasons typically have wrinkles, age spots, spider veins, acne scars, or other signs of photoaging.
Patients need to be in good health and at least 18 years of age for all laser treatments.
What Conditions Can Laser Therapy Treat?
Laser therapy has many applications in medicine and cosmetics.
Medical lasers are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in almost all medical disciplines, including dermatology, ophthalmology, dentistry, gastroenterology, urology, neurosurgery, cardiology, etc.
Some laser therapy indications include:
- Vascular lesions
- Pigmented lesions
- Urological and genital lesions
- Benign and malignant tumors
- Eye conditions (e.g., glaucoma)
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Kidney stones
- Wound healing
- Burn scars
- Acne
- Psoriasis
- Eczema
- Actinic keratosis
- Bowen’s disease
- Caries and other dental issues
Lasers are also used to address aesthetic skin concerns. Laser resurfacing is a type of laser therapy that helps improve the following conditions:
- Wrinkles
- Hyperpigmentation
- Acne scars
- Spider veins
- Skin laxity
- Uneven skin tone
What Are the Benefits of Laser Therapy?
The benefits of laser therapy include:
- A wide range of medical uses
- Reducing premature aging signs
- More precise than a surgical knife
- Generally safe and well-tolerated
- Shorter recovery time than with traditional surgery
- Reduces the risk of side effects (e.g., pain, swelling, and scarring)
How to Prepare for Laser Therapy
During the consultation, the medical provider explains to the patient how to prepare for a laser treatment.
Patients usually need to stop taking blood-thinning medication and supplements, such as aspirin, vitamin E, ibuprofen, fish oil, etc. Sometimes, they are advised to take antibiotics to prevent infection or to use other medications.
Medical providers recommend refraining from smoking and alcohol for several days before the treatment to reduce the risk of side effects. Laser resurfacing also requires patients to avoid sun exposure for a few weeks before the treatment.
What to Expect During Laser Therapy
Depending on the laser therapy type, the procedure is performed in a med spa, clinic, or a hospital.
In the case of a PDT procedure, the patient first receives photosensitizers as a drink, injection, or topical drug and returns to the clinic after a few hours to activate the medication with a laser that heats the target area.
In laser surgery on an internal organ, a small tube (endoscope) is inserted in the body to find abnormal cells and treat them with a laser beam. In eye surgery, the laser focuses on the cornea to cut and remove damaged tissue.
With laser resurfacing, the laser light is applied directly on the skin to treat the skin concern.
The procedure can last between 15 minutes and several hours (for more complicated tumor surgeries).
How Painful Is Laser Therapy?
Laser therapy is not painful because medical providers use numbing creams, sedatives, local anesthetics, or general anesthesia. Recovery may be painful, depending on the severity of the treated medical or aesthetic condition and the type of laser procedure. If needed, patients can take over-the-counter pain medications to relieve pain and discomfort after the treatment.
Laser Therapy Results
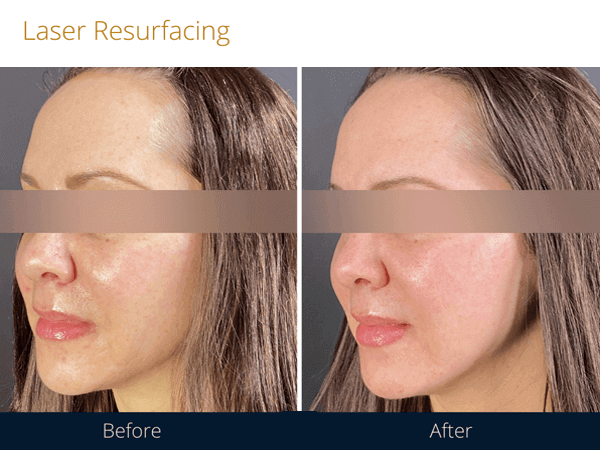

The results of laser therapy vary depending on the treated condition and laser type.
In medical procedures, lasers relieve pain, reduce inflammation, regenerate tissues, eliminate tumors, and more.
Laser resurfacing rejuvenates the skin and improves various skin issues, including sun damage, hyperpigmentation, skin laxity, and scars. Ablative lasers significantly transform the skin after just one treatment. The results become visible after several weeks or, in some cases, several months. Non-ablative lasers are less invasive and provide subtle but noticeable results. They require several treatments.
How Long Do Laser Results Last?
The longevity of laser therapy results varies. In cases of eye surgery and some tumors, they can be permanent. For cosmetic skin concerns, the results depend on the type of laser and the severity of the condition. The results of ablative lasers can last several years. The results of non-ablative procedures usually last for 6 – 12 months. Maintenance treatments extend the results.
Laser Therapy Aftercare
Laser therapy aftercare varies with different laser treatments. The following are some general aftercare guidelines:
- Avoid strenuous sports.
- Avoid alcohol and nicotine.
- Don’t use harsh skincare products and makeup.
- Take painkillers if needed.
- Use cold compresses if needed.
- Avoid high heat and UV exposure.
Laser Therapy Side Effects
Like any medical procedure, laser therapy comes with risks of certain side effects. They vary depending on the laser therapy type, device, the treated condition, and the patient’s medical status.
Common side effects include:
- Bleeding
- Swelling
- Scarring
- Pain
- Infection
- Fever
- Pigmentation
Who Should Not Do Laser Therapy?
Contraindications for therapeutic and cosmetic laser treatments are relative to the type of therapy.
Generally, the following conditions increase the risk of complications:
- Pregnancy
- Autoimmune diseases
- Certain blood disorders
- Meningitis
- Epilepsy
- Neuropathy
- Steroid use
- Skin abnormalities
- History of melasma
Lasers shouldn’t be applied over the thyroid gland, the gravid uterus, and directly over the eyes. Tattoos and permanent makeup should be avoided, unless the purpose of the treatment is ink removal.
Laser Therapy FAQ
Answers to these questions from first-time laser patients will further help you determine if the treatment is right for you.
What Is the Most Painful Place to Laser?
Many laser treatments involve little to no pain thanks to numbing creams, sedatives, and anesthesia. However, patients can feel pain and discomfort during intense, ablative laser resurfacing and medical procedures.
Laser hair removal can cause pain and discomfort in areas with a lot of nerve endings, thinner skin, and dark, coarse hairs. Such areas include the bikini line, underarms, upper lip, and chest (for men).
How Much Does Laser Therapy Cost?
The cost of laser therapy depends on the treatment type.
Laser resurfacing costs approximately $1,800 per session, according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
At Vibrant Skin, the cost of laser treatments ranges from $150 for small area hair removal to $2400 for Halo Pro laser. Halo costs $1200, and the BBL treatment costs $349.
Is Laser Therapy Covered by Insurance?
Cosmetic laser procedures are generally not covered by health insurance since they are considered elective. However, laser treatments that are medically necessary (such as for tumor removal, treatment of vascular abnormalities, or certain vision-correcting surgeries) may be covered in part or in full, depending on the policy. Coverage varies, so it is important to confirm details with your insurance provider.
Conclusion
Lasers are powerful devices with an expanding list of medical and cosmetic uses. However, they may cause harm if used incorrectly. Always seek licensed and experienced medical professionals to reduce the risk of adverse effects and ensure effective laser therapy.


